In this article, we will explore the incredible benefits of honey in boosting the immune system. Honey has long been celebrated for its natural healing properties, and its role in supporting our body’s defense system is no exception. From soothing sore throats to fighting off harmful bacteria, honey is a powerhouse of nutrients that can provide a much-needed boost to your immune health. Join us as we uncover the science behind honey’s immune-boosting powers and discover the delicious ways you can incorporate this golden elixir into your daily routine. Prepare to be amazed by the wonders of honey and its contribution to a stronger, healthier immune system.
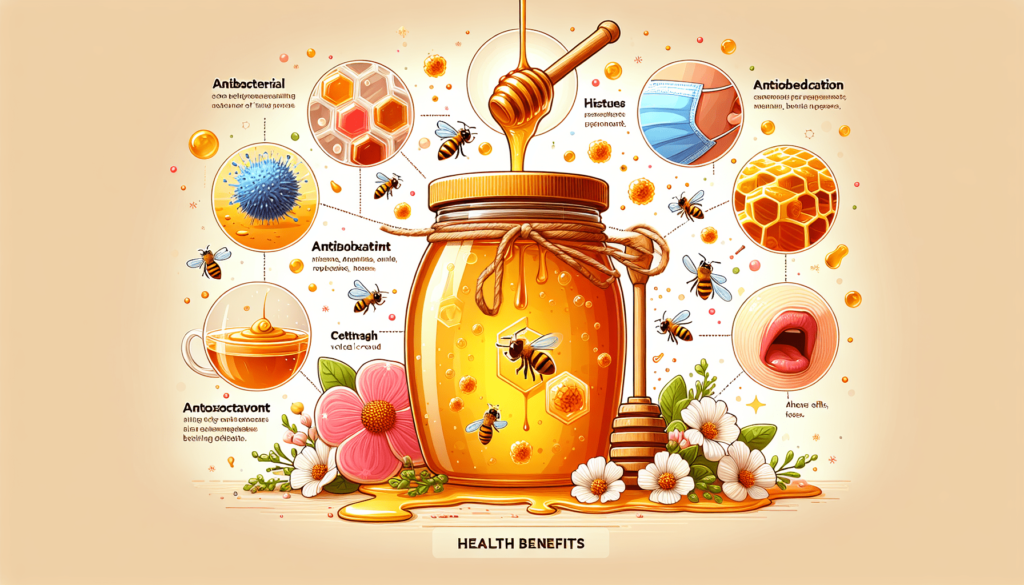

Antibacterial Properties
The presence of hydrogen peroxide
One of the key reasons why honey has antibacterial properties is due to the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is produced by an enzyme called glucose oxidase, which is found in honey. This enzyme breaks down glucose and produces hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct. Hydrogen peroxide is known for its antimicrobial properties, making honey an effective natural remedy for fighting bacteria.
The role of glucose oxidase enzyme
Glucose oxidase is an enzyme present in honey that plays a crucial role in its antibacterial properties. This enzyme is responsible for breaking down the glucose in honey and converting it into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Gluconic acid creates an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of bacteria, while hydrogen peroxide has potent antimicrobial properties. Together, these compounds make honey an effective natural antibacterial agent.
Effect on harmful bacteria
Honey has been shown to have a significant effect on harmful bacteria. Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against a wide range of bacteria, including strains that are resistant to antibiotics. The antimicrobial properties of honey help to inhibit the growth and spread of these bacteria, making it a valuable tool in combating bacterial infections. Regular consumption of honey can help prevent the colonization of harmful bacteria in the body and promote overall health.
Antioxidant Effects
Flavonoids and phenolic compounds
Honey contains various antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Flavonoids are a type of polyphenol that have strong antioxidant properties. Phenolic compounds, such as caffeic acid and gallic acid, also contribute to the antioxidant effects of honey. These antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative damage to cells. By reducing oxidative stress, honey can protect the body from various chronic diseases and support overall health.
Neutralization of free radicals
Free radicals are generated naturally in the body as a byproduct of various metabolic processes. However, an excess of free radicals can lead to oxidative stress, which can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases, including heart disease and cancer. The antioxidants present in honey help neutralize free radicals, preventing them from causing harm to the body. Regular consumption of honey can support the body’s antioxidant defense system and reduce the risk of oxidative damage.
Prevention of oxidative stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s antioxidant defenses. This imbalance can lead to cellular damage and contribute to the development of chronic diseases. The antioxidants in honey play a crucial role in preventing oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals and reducing their harmful effects. By reducing oxidative stress, honey can help protect against conditions such as inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Anti-inflammatory Benefits
Reduction of inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of various diseases, such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. Honey has been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body. The antioxidants present in honey help suppress the production of pro-inflammatory substances, thereby aiding in the management of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Beneficial impact on respiratory system
Honey has long been used as a natural remedy for respiratory ailments, such as coughs, colds, and allergies. Its anti-inflammatory properties can benefit the respiratory system by reducing inflammation in the airways and promoting easier breathing. Honey also acts as a natural expectorant, helping to loosen mucus in the respiratory tract and alleviate congestion. These soothing effects make honey an excellent choice for relieving respiratory symptoms and promoting respiratory health.
Suppressing the release of pro-inflammatory substances
When the body experiences inflammation, certain substances called cytokines and prostaglandins are released. These substances contribute to the inflammatory response and can cause discomfort and pain. Honey has been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties that help suppress the release of these pro-inflammatory substances. By reducing their levels in the body, honey can alleviate inflammation and provide relief from various inflammatory conditions.

Immune System Boost
Enhancing cytokine production
Cytokines are small proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system’s response to infection and inflammation. Honey has been shown to stimulate the production of certain cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β). These cytokines help regulate immune responses, promote the activation of immune cells, and enhance the body’s defense against pathogens. By enhancing cytokine production, honey can boost the overall functioning of the immune system.
Stimulating the production of antibodies
Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to the presence of foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses. Honey has been found to stimulate the production of antibodies, helping to strengthen the immune response and enhance the body’s ability to fight off infections. Regular consumption of honey can support the production of antibodies, thereby bolstering the immune system’s defenses against pathogens.
Promoting the activity of white blood cells
White blood cells are essential components of the immune system that help fight infections and protect the body from foreign invaders. Honey has been shown to promote the activity of white blood cells, enhancing their ability to detect and destroy pathogens. By boosting the activity of white blood cells, honey can strengthen the immune system and improve overall immune function. This can result in a reduced risk of infections and improved overall health.
Alleviating Allergy Symptoms
Reduction of histamine release
Histamine is a compound released by the immune system in response to allergens, such as pollen or dust. It is responsible for triggering allergy symptoms, such as sneezing, itching, and watery eyes. Honey has been found to possess antihistamine properties, helping to reduce the release of histamine and alleviate allergy symptoms. Regular consumption of honey, especially locally sourced varieties, can provide natural relief from seasonal allergies.
Potential desensitization
Studies have suggested that consuming honey from local sources may help desensitize individuals to common allergens found in their environment. Local honey contains small amounts of pollen from local plants, which can help the body build up tolerance to these allergens over time. While more research is needed to fully understand this potential benefit, some individuals have reported reduced allergy symptoms after regularly consuming local honey.
Managing seasonal allergies
Seasonal allergies, also known as hay fever, can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily life for many individuals. Honey has been used as a natural remedy for managing seasonal allergies due to its potential antihistamine properties and ability to reduce histamine release. Regular consumption of honey, particularly during allergy seasons, may help alleviate symptoms such as sneezing, congestion, and itchy eyes. It is important to note that individual responses to honey may vary, and it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Soothing Sore Throats
Coating the throat
Honey has been used for centuries as a soothing remedy for sore throats. Its thick consistency allows it to coat the throat, providing a protective layer that can help alleviate discomfort and reduce irritation. The antimicrobial properties of honey also contribute to its soothing effects, helping to address the underlying cause of a sore throat and promote healing.
Cough suppressant properties
Honey has been found to possess natural cough suppressant properties, making it an effective remedy for relieving cough symptoms. Whether caused by a cold or allergies, coughing can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life. The viscous nature of honey helps soothe the throat and calm the cough reflex. Additionally, the antimicrobial properties of honey can help address any underlying infections that may be causing the cough.
Relieving throat inflammation
Inflammation of the throat often accompanies sore throat and cough symptoms. Honey’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce throat inflammation and alleviate discomfort. By soothing the inflamed tissues, honey provides relief and promotes the healing process. Whether taken alone or added to warm water or tea, honey is a natural and effective option for soothing sore throats and promoting overall throat health.
Digestive Health
Prebiotic properties
Honey contains prebiotic compounds, which are non-digestible substances that promote the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria. Prebiotics act as food for probiotics, the healthy bacteria that reside in the gut and support digestion and overall gut health. Regular consumption of honey can help nourish the gut microbiota, enhancing digestive health and promoting proper nutrient absorption.
Supporting beneficial gut bacteria
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in digestion and overall health. Honey has been found to support the growth and activity of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species. These bacteria aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, strengthen the gut barrier, and support immune function. By promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, honey can contribute to a healthy gut ecosystem and improve digestive health.
Enhancing nutrient absorption
Proper nutrient absorption is essential for overall health and well-being. Honey has been shown to enhance nutrient absorption, particularly for certain vitamins and minerals. Its prebiotic properties and influence on the gut microbiota contribute to improved digestion and nutrient absorption. By enhancing nutrient absorption, honey supports overall nutritional status and helps ensure the body receives the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning.
Wound Healing
Antimicrobial effects
Honey has long been recognized for its wound healing properties. One of the key factors contributing to its effectiveness is its antimicrobial effects. The enzymes and low pH in honey create an inhospitable environment for bacteria, preventing infection and promoting wound healing. Honey has been used topically to treat various types of wounds, such as cuts, burns, and ulcers, with positive outcomes.
Hydrogen peroxide production
As mentioned earlier, honey contains glucose oxidase, an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is a natural antiseptic that helps kill bacteria and prevent infection in wounds. When honey comes into contact with wound fluids, glucose oxidase breaks down glucose and releases hydrogen peroxide, creating a clean and sterile environment that supports the healing process. This unique property of honey contributes to its efficacy in wound healing.
Promoting tissue regeneration
In addition to its antimicrobial effects, honey has been found to promote tissue regeneration. It provides a moist environment that prevents the formation of scabs and supports the growth of new tissue. The natural sugars in honey draw water into the wound, keeping it hydrated and aiding in the formation of healthy granulation tissue. This promotes faster healing, reduces scarring, and improves overall wound closure.
Cough and Cold Relief
Soothing cough symptoms
Honey has long been used as a natural remedy for cough relief. Its viscous texture helps coat the throat, providing soothing relief from throat irritation and reducing coughing. The antimicrobial properties of honey also contribute to its effectiveness in managing cough symptoms. Whether taken directly or added to warm water or tea, honey can provide natural and gentle relief from coughs, particularly those associated with colds and respiratory infections.
Loosening mucus
Coughing is often accompanied by the production of excess mucus, which can be difficult to expel. Honey has been found to have expectorant properties that help loosen and thin mucus, making it easier to cough up and clear the airways. By reducing mucus congestion, honey can provide relief from coughing and promote better respiratory function.
Reducing cough frequency and severity
The soothing properties of honey, along with its ability to suppress coughs and loosen mucus, can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of coughing episodes. Unlike over-the-counter cough medications that may have unwanted side effects, honey offers a natural and safe alternative for individuals seeking relief from cough symptoms. However, it is important to note that honey should not be given to infants under one year of age due to the risk of botulism.
Anticancer Properties
Potential tumor growth inhibition
Studies have shown that some compounds present in honey may possess properties that inhibit tumor growth. Certain types of honey, such as Manuka honey, have been found to exhibit cytotoxic effects on cancer cells, causing them to undergo cell death. The specific mechanisms by which honey exerts its anticancer effects are still being investigated, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential in cancer treatment and prevention.
Inducing apoptosis in cancer cells
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a natural process that helps regulate cell growth and eliminate damaged or abnormal cells. Honey has been found to induce apoptosis in cancer cells, which can help inhibit their growth and prevent the spread of cancer. The compounds present in honey, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, play a crucial role in this process, making honey a potential adjunctive therapy for cancer treatment.
Protecting DNA from oxidative damage
Oxidative damage to DNA is a key factor in the development of cancer. Honey’s antioxidant properties help protect DNA from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of mutations and potential cancerous transformation. By neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, honey supports DNA integrity and contributes to a decreased risk of cancer development.
In conclusion, honey offers a wide range of health benefits due to its antibacterial properties, antioxidant effects, anti-inflammatory benefits, immune system-boosting properties, allergy symptom relief, soothing effects on sore throats, digestive health support, wound healing properties, cough and cold relief, and potential anticancer properties. Whether consumed or used topically, honey can be a valuable natural remedy for various health concerns. Incorporating honey into your daily routine can contribute to improved overall health and well-being.